The Importance of Speed in Basketball

Basketball is a game of intensity and quick transitions. A key determinant of success in this adrenaline-fueled sport is speed. But when we say ‘speed,’ we’re not merely referring to how fast a player can sprint from one end of the court to the other. Speed in basketball is multidimensional—it encompasses physical agility, mental acuity, and strategic adaptability.
Physical Speed and Agility
Strength and agility allow an athlete to exercise better control. An agile athlete can change direction quickly and outrun his/her opponent.
Norbert Juma, Editor of EverydayPower.com
At its core, basketball requires physical speed. The ability to swiftly maneuver around the court, both offensively and defensively, can have a profound impact on a player’s performance. The ability to move confidently allows players to reach the basket quicker, defend more effectively, and react to changes in the game instantaneously. It can mean the difference between a well-executed fast break and a missed opportunity.
Speed also ties in closely with agility—the capacity to change direction quickly and efficiently. Agile players are able to dodge defenders, swiftly shift between offensive and defensive modes, and maintain control of the ball under pressure. As Bill Russell famously said, “Quickness is the essence of the game.”
Mental Agility and Decision-Making
“Speed is not just about moving fast;
John Wooden
it’s about making fast decisions.”
Speed, however, is not solely a physical attribute. Cognitive agility —the ability to quickly process information, make decisions, and react accordingly—is equally vital in basketball. When a player has the ball, they need to rapidly assess the situation, consider their options, and make a decision, all in a matter of seconds. This mental agility significantly influences a player’s effectiveness on the court.
Quick decision-making can contribute to efficient plays, reduced turnovers, and well-timed passes. It’s a key factor in running a smooth offense and making split-second decisions that can change the course of the game. As the great basketball coach John Wooden once stated, “Failure is not fatal, but failure to change might be.”
Strategically Fast and Adaptable?
Finally, strategic speed—the capability to adapt game plans in response to the opponent’s tactics—plays an instrumental role in basketball. In a dynamic and unpredictable game, a team’s ability to quickly adjust their strategy can be the difference between winning and losing.
Coaches and players must observe the opposing team, recognize patterns, anticipate their moves, and adjust their own tactics on the fly. Successful teams are those that can swiftly shift strategies without losing momentum, capitalizing on their strengths and exploiting their opponents’ weaknesses.
Training for Speed
Given its vital role in basketball, it’s essential for players to train for speed. This includes both physical training—such as sprinting drills, agility ladders, and plyometric exercises—and cognitive training, such as learning to read the game, understanding different strategies, and practicing quick decision-making.
But as Michael Jordan suggested, it’s not about wishing for it to happen; it’s about making it happen. Consistent effort, perseverance, and a growth mindset are required to improve speed. Every practice, every drill, every game is an opportunity to become faster—physically, mentally, and strategically.
Do you have “The Need for Speed”?
I feel very comfortable going at full speed.
Steve Nash, NBA All Star and League MVP
In basketball, speed is far more than just a physical trait—it’s a fundamental element that permeates every aspect of the game. From physical agility to mental acuity, from strategic adaptability to constant learning, speed in its various forms can give players and teams a significant advantage.
In the words of the great basketball coach, Phil Jackson, “Basketball is a sport that involves the subtle interweaving of players at full speed to the point where they are thinking and moving as one.” Speed—whether physical, mental, or strategic—is at the heart of this interweaving, and mastering it is crucial to basketball success.
So, whether you’re a player aiming to improve your game or a coach looking to guide your team to victory, remember—the importance of speed in basketball can never be overstated. As the game continues to evolve, speed remains a key component, underscoring its timeless relevance in this fast-paced sport.
Have you commented yet?
We would love to hear what you thought of this article. What can you add to this topic? How does it compare to our other articles... better, worse, different?










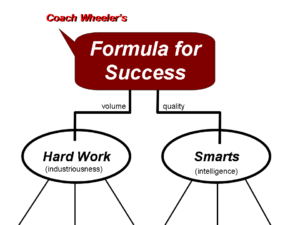 This probably won’t sound earth shattering but it should make immediate sense when you think about it. “The
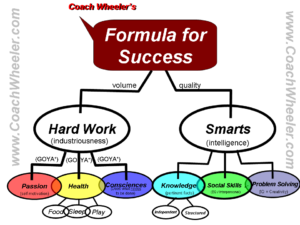
This probably won’t sound earth shattering but it should make immediate sense when you think about it. “The 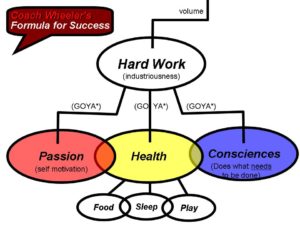 The Formula for Success has 3 parameters under “Hard Work”. They are (1) Passion, (2) Health and (3) Consciences. Let’s look at each in more depth.
The Formula for Success has 3 parameters under “Hard Work”. They are (1) Passion, (2) Health and (3) Consciences. Let’s look at each in more depth.
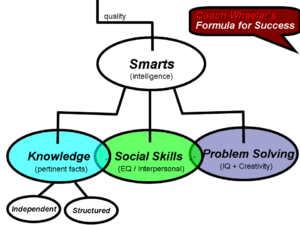 The second major component of Success is “Smarts” or “general intelligence”. Coach Wheeler breaks this down into 3 parts, (1) Knowledge, (2) Social Skills and (3) Problem Solving. Going back to Jordan B. Peterson, he has said that the studies show intelligence, as measured by IQ, is incredibly difficult to improve. On the other hand, Knowledge can continually be accumulated and you can gather facts or ideas that you can use across a wide variety of situations. Coach Wheeler also added Social Skills to his model for success and we will discuss how to build and leverage them more below.
The second major component of Success is “Smarts” or “general intelligence”. Coach Wheeler breaks this down into 3 parts, (1) Knowledge, (2) Social Skills and (3) Problem Solving. Going back to Jordan B. Peterson, he has said that the studies show intelligence, as measured by IQ, is incredibly difficult to improve. On the other hand, Knowledge can continually be accumulated and you can gather facts or ideas that you can use across a wide variety of situations. Coach Wheeler also added Social Skills to his model for success and we will discuss how to build and leverage them more below.


 This post is about the “Things I Know” when it comes playing basketball “the correct way”, i.e. the way that I like my teams to play. Each of these short “Things I Know” is followed by an action that players should carry out in the described situation.
This post is about the “Things I Know” when it comes playing basketball “the correct way”, i.e. the way that I like my teams to play. Each of these short “Things I Know” is followed by an action that players should carry out in the described situation. The one basketball season ends and another basketball year begins. If you are only playing and working on your game during the “official school season” than you are missing out. Below are the 4 sections / timelines that make up the “4 part basketball year” plus the off-season. Let’s start with the day after your school season ends…
The one basketball season ends and another basketball year begins. If you are only playing and working on your game during the “official school season” than you are missing out. Below are the 4 sections / timelines that make up the “4 part basketball year” plus the off-season. Let’s start with the day after your school season ends… What does it mean for a player to “take their game to the next level”? It sounds like a good thing but without understanding the meaning it is hard to get there, right?
What does it mean for a player to “take their game to the next level”? It sounds like a good thing but without understanding the meaning it is hard to get there, right? I coached this player as part of an AAU team when he was a freshman and he was a pretty good shooter. I won’t “name names” since I don’t want to embarrass him. Plus the advice could apply to a number of players.
I coached this player as part of an AAU team when he was a freshman and he was a pretty good shooter. I won’t “name names” since I don’t want to embarrass him. Plus the advice could apply to a number of players.
 The lunge is another underrated drill. In fact,
The lunge is another underrated drill. In fact,